6 steps to improving Physical Sciences results – A note to parents
Dinesh Krithallal • October 21, 2020
I have been involved in Physical Sciences education for more than 27 years. My experience in teaching the subject, as well as my involvement in the National Matric Final Examinations, has helped me identify ideas that assist in improving Physical Sciences proficiency and it gives me great pleasure to share these ideas with you.
Download the Infographic
Nobody learns to walk from a textbook. It is the same as developing a scientific mind. We learn to walk after trying what seems to work better for us during that stage of our development. An important part of this learning takes place with help from our parents. Imagine how much longer it would have taken us to walk without their encouragement and support.
While we pay homage to our loving parents and guardians and gracefully say a big thank you, I would like to remind parents that their involvement in their child’s education does not stop with facets they are not proficient in, for example, Mathematics or Science. Just as a parent or guardian who cannot walk can encourage and support a young child to walk without assistance, a parent who is not proficient in Mathematics or Science can assist their child to improve in these subjects.
Ideas on how this can work:
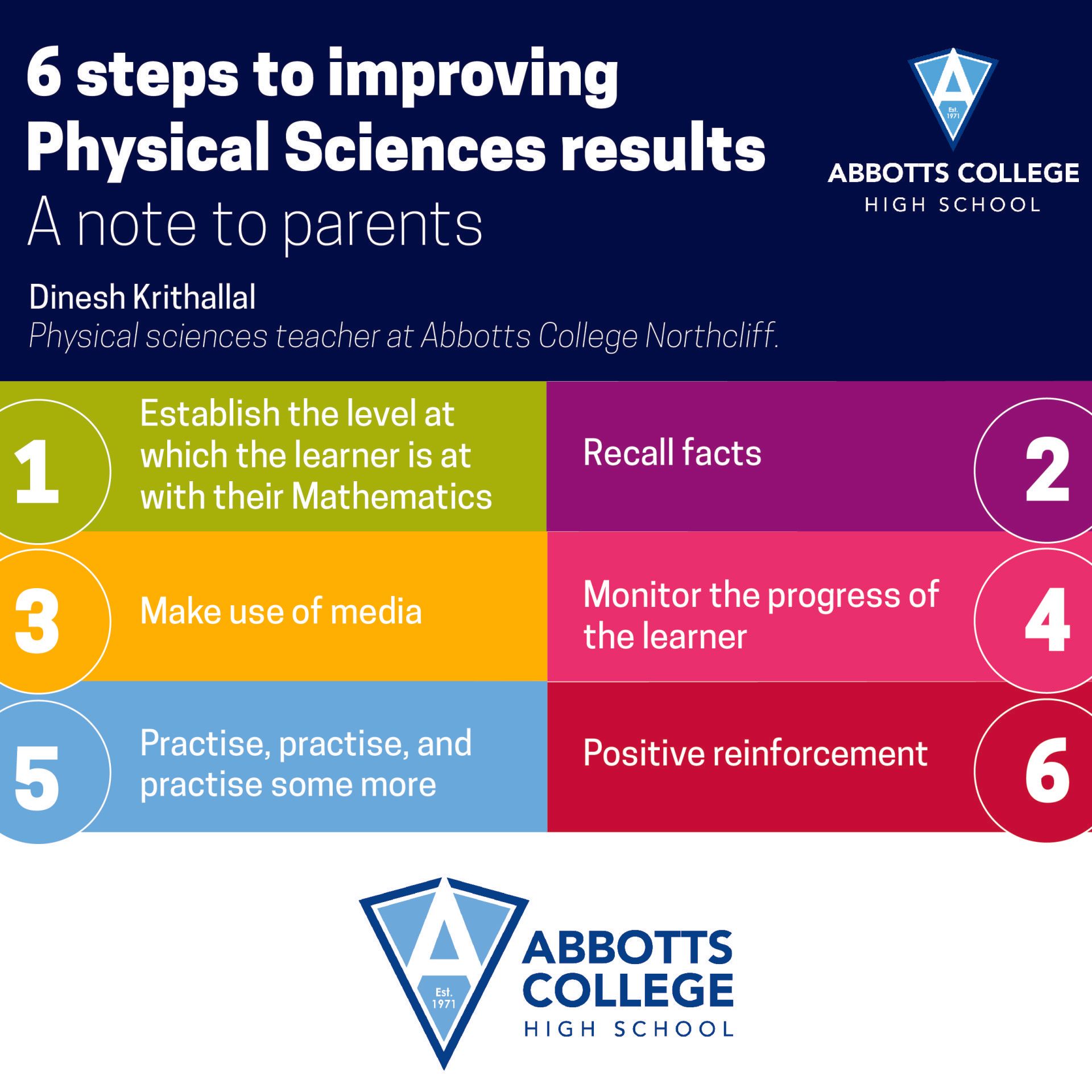
1. Establish the level at which the learner is at with their Mathematics
My first suggestion is to establish the level at which the child is with Mathematics. If there are gaps then it may be a good idea to get a set of Grade 8, 9, and 10 Mathematics study aids, like PRACTMATHS by Seeliger and Mouton. The study aid that you choose must have complete solutions and not just the answers. It would have taken the child a whole year to complete the Grade 8 Mathematics syllabus but may just take 6 to 8 weeks to complete the same syllabus the second time around. Then get the child to move onto the Grade 9 Mathematics syllabus and then onto the Grade 10 Mathematics syllabus. Once the child completes the above Mathematics syllabi, he/she will have grown confident in his/her Mathematics abilities. The growth of confidence is of paramount importance to assist learners in their academic growth.
Once you have built the confidence that is required in the learner’s Maths abilities, you can then look forward to improving Physical Sciences skills. Please note that Mathematics and Physical Sciences are both practise subjects and as such, the learners will constantly need to apply their knowledge to problem-solving as often as possible. We cannot expect to use the jug and mug method of dispensing skills to learners.
2. Recall facts
The other skill to focus on is the ability to recall facts contained in terminology, definitions, or theory. The learner must be able to grow his/her memory and recall skills. The good news is that growing memory and recall skills are similar to growing muscles. Just as someone who focuses on a certain muscle group during fitness training sees results in that muscle group, a learner who practises in Maths and Physical Sciences will see the appropriate results from his/her investment of time. Learners must be encouraged to set goals and work towards their goals.
We are often led to believe that the sciences do not require the swotting of facts. This is not true. While most concepts are mastered with the focus being on the concept, there are many facts to remember. Make a list of these facts and ensure that the learner knows these facts timeously. Do not accept the excuse that the learner does not understand the concept and, therefore, cannot learn the facts. This is an age-old excuse for not making the effort to learn terminology, theory, and definitions, so be tactful when approaching this excuse from learners.
My suggestion is to get the learner to make flashcards. The flashcards must have, for example, the term on the front and the definition on the back. This way a parent may test the concept without even remembering or knowing the concept. I would suggest that learners take an A4 sheet of printing paper and make four flashcards. Learners may punch the cards using a paper punch. These flashcards can then be filed. The learner can always add to their bank of flashcards as they progress from Grade 10 to Grade 12 in Physical Sciences.
3. Make use of media:
We must encourage the use of media (such as YouTube) to view videos on topics that the learner may find challenging. Research skills are important in all subjects.
4. Monitor the progress of the learner:
Set aside time to monitor the learner’s Maths homework. Ask the learner to complete all other homework in your absence but set aside about 20 minutes a day to monitor the learner’s Maths homework. A Physical Sciences learner cannot afford to fall behind in Mathematics. A poor Maths mark is crippling to performance in Physical Sciences.
Sir Richard Branson once said: “if you expect to collect milk from a cow, don’t take a chair and sit in the middle of the field where the cow is and expect the cow to come to you and give you the milk you require”. Go out there with a plan and make it work. Making it work may involve changing strategies along the way. Making it work may even involve starting again with a new strategy. Be amenable to change as change is a constant in life.
5. Practise, practise, and practise some more:
Since Physical Sciences, as well as Maths, are both practise subjects, learners must be encouraged to practise these subjects constantly. Working through past papers is a proven strategy.
6. Positive reinforcement:
One must not forget the benefits of positive reinforcement and every little bit of progress made must be celebrated with praise.
I wish you well on your journey to improving Physical Sciences with your child. At first, it will be hard work, just like walking was once hard work. Give it some time and soon the learner will be jogging and even sprinting in these subjects.
To learn more tips from our teachers and educational experts, click here
To learn more about Abbotts College, click here
To learn about the Abbotts College experience, click here
Feel free to call or email one of our correspondents.

As the preliminary and final examinations approach, both students and parents or guardians often experience heightened anxiety and stress. This guide provides practical strategies to help parents and guardians support their children through this critical phase of their academic journey. 1. Foster Effective Organization Create an environment conducive to studying by providing a quiet, well-lit study space equipped with essential stationery. Collaborate with your child to develop a structured study timetable to set clear expectations and promote disciplined preparation. Encourage the use of resources such as past question papers, which serve as valuable tools for revision and practice. 2. Maintain Daily Check-Ins Schedule regular, intentional conversations, such as during dinner, to discuss your child’s progress. Inquire about their experience with the day’s examination paper, adherence to their study schedule, and their feelings about upcoming tests. These check-ins foster open communication and allow you to gauge their emotional and academic state. 3. Minimize Distractions Help your child stay focused by keeping electronic devices like phones, tablets, and gaming consoles out of reach during study sessions. Set boundaries on screen time and social media access to prevent procrastination. While challenging, limiting Wi-Fi access during study hours can significantly enhance productivity. 4. Support Emotional Awareness Encourage your child to identify and articulate their emotions, such as anxiety, stress, or fatigue . Recognizing these feelings is the first step toward addressing them effectively. Discuss coping strategies to help them navigate emotional challenges during this period. 5. Teach Self-Regulation Techniques Guide your child in practicing self-regulation to manage stress. Techniques include: Breathing Exercises : Inhale deeply for four seconds, hold for four seconds, exhale for four seconds, and repeat. Sensory Focus : Identify five things they can see or hear to ground themselves in the moment. Tactile Stimulation : Hold a cold object to shift focus and reduce anxiety. These methods can help your child regain calm and focus during stressful moments. 6. Promote a Balanced Routine Prolonged study sessions late into the night can lead to burnout. Monitor your child’s study habits and encourage breaks to maintain balance. Plan activities such as outings with friends, a family meal, or short recreational periods with access to devices. Engaging in non-academic activities, like helping prepare dinner, can provide a refreshing change of focus. 7. Prioritize Self-Care Support your child’s well-being by ensuring they: Eat nutritious, regular meals. Get at least eight hours of sleep by limiting screen time before bed. Engage in physical activities such as walking, jogging, yoga, dancing, or gym workouts. These practices help alleviate stress and anxiety, which are common during examination periods. 8. Practice Empathy and Patience The examination period can be emotionally taxing for both students and parents. Approach your child with empathy, actively listening and offering guidance without criticism. This fosters a supportive environment, bolstering their mental health and sense of inclusion. By implementing these strategies, parents and guardians can play a pivotal role in helping their children navigate the challenges of examinations with confidence and resilience. Good luck to all the Grade 12 students with the upcoming examinations - you most certainly can do it!

Key Takeaways Personalised learning helps teens thrive by focusing on their unique strengths, interests, and goals. This approach encourages students to take ownership of their studies, building confidence and responsibility. Teachers play a vital role by adapting lessons and feedback to suit individual learning styles. Alternative education models often integrate personalised learning to support students who need flexibility. Whether you’re exploring private high schools in Pretoria , Centurion high schools , high schools in Northcliff , Johannesburg, or high schools in Cape Town with no uniform , personalised learning can help students reach their full potential in any environment. Every young person has a unique story, but in the wrong school, that story might never be realised and celebrated. The right school, however, ensures that each story is heard and every student lives up to their full potential. Enter personalised learning: Environments where young people are seen, supported and encouraged to explore who they are and want to be in the world. When parents and students walk into a school which prides itself on being student-centered, they immediately feel this difference. In my 30 years in education, I’ve been continually inspired by what young people can achieve when given the right tools, space, and support. Success is about so much more than academic results, it also includes emotional and social growth. When students are free to express themselves, they experience deeper learning, and greater personal well-being and self-confidence. This freedom builds communication skills, sparks creativity, and fosters critical thinking, developing them into confident and capable young adults. TAILORING EDUCATION TO INDIVIDUAL NEEDS When schools shift to personalised learning, something transformative happens: Students stop feeling like just another face in the crowd and instead, they become active participants in their education. With tools like MAP assessments, teachers gain valuable insights into where a student excels and where they need support. This data informs learning plans tailored to each student’s pace and style. Some students benefit from short videos or visual aids, while others prefer hands-on tasks or one-on-one support. Platforms like Khan Academy and adaptive learning apps help teachers meet these diverse needs with precision. This model creates a more dynamic learning environment, where a struggling student can revisit a topic until it makes sense. Advanced learners are able to move on to more challenging material without waiting. Each student progresses at their own pace, in a way that works for them. BEYOND ACADEMICS The benefits of personalised learning go well beyond the classroom. Students build emotional resilience when their needs are recognised and met. Social development naturally follows as they take ownership of their learning and grow in confidence. Personalised learning doesn’t demand perfection, but invites growth. Schools become places of discovery, where students study not only the curriculum, but also discover who they are and what they’re capable of. If you are wondering whether high schools can change lives by embracing individuality, just watch a student light up when talking about a subject they love. Look at the learners who feel safe enough to speak up, take risks, and aim higher. UNLOCKING TRUE POTENTIAL When schools see students not as numbers, but as individuals with dreams and potential, education becomes truly impactful. Personalised learning is not a trend, it is a return to what learning should be: human, responsive, and empowering. As educators, parents, and communities, we must create environments where every student feels valued and every voice matters. Because when we embrace students for who they really are, we unlock the door to who they’re meant to become. FAQs How does alternative education in South Africa support personalised learning? Alternative education South Africa supports personalised learning by offering flexible teaching styles that focus on each student’s needs and learning preferences Do any high schools in Cape Town allow students to wear their own clothes? Yes, high schools in Cape Town with no uniform , like Abbotts College Rondebosch, allow students to dress casually, promoting individuality alongside academic success. How does personalised learning work in Centurion schools? Centurion schools like Abbotts College use personalised learning by adapting lessons to suit each student’s strengths and goals, helping them build confidence and achieve better results. How do I decide which high school in Centurion area is best? To choose the best high school in Centurion area , consider the school’s teaching style, support systems, and how well it aligns with your teen’s academic goals and personal growth. Why might parents choose private high schools in Johannesburg for their teens? A5. Private high schools in Johannesburg provide personalised learning, strong academic programmes, and individual support to prepare teens for university and life beyond school.

In the wake of the mid-year exams, there is much that parents and students can learn from their results, which should be used to consider the way forward, an education expert says. “I was fortunate to have one child who was very diligent as a scholar, starting to study way ahead of the exams, even from the lower grades, using her midterm break to study year after year. She never had to be asked to go and study and her study breaks were actual breaks from studying,” says Mignonne Gerli, Principal: Abbotts College Pretoria East. “This was not true for all my children. Another of my children thought that studying the day before the exam would do just fine. I remember always catching this child on a study break or as she had just finished studying. I can confidently say that I never, in five years, caught her studying. You can imagine the fights and stress (felt by me) during this time.” As parents, we know how important it is to achieve good results at school. Prior to Grade 11 and 12, students already need to have developed a mature and diligent work ethic. “We know which doors can be opened and which firmly shut, based on your school results,” says Gerli. “For this reason, we fight the good fight which means that exam periods can be extremely stressful and highly unpleasant in many households. We try various methods to cajole our less than diligent children to put effort into their studies and in some cases loathe the day that the reports are published.” Whether exam time is a breeze for you as a parent, with your model child, or absolute hell, with your sweet/funny/kind but less committed child, the end of the exams and results need to be reflected upon. And for those who suffered through the past exams, it is time to come up with different strategies for the next set of exams. “Reflection for those who appear to prepare well for exams, will take the form of considering whether their study methods were effective or if they need help with the way in which they study.” “During these exams, I watched my one granddaughter study. “Not once did I catch her on a break on the days she was with us. What I also noticed was that she studies by copying out the textbook, not something that can be remedied when she is shoulder deep into the exams. This is not an effective way to study and she will definitely need to be taught better study methods in preparation for her next exams.” What have you as a parent noticed about your child’s study methods? Can you assist or will you need a professional to help with better study methods? “Students who achieved excellent results for their exams can reflect on why they did so well and how they can build on this going forward. “The students who put little to no effort into their preparation for the exams, will need guidance and assistance from their parents to try remedy their approach to their work. There needs to be an open, calm discussion about why they did not study for the exams and what would motivate them to study and put effort into their preparation for their next exam session.” Approaches could include: Negative consequences for poor effort, such as having their phones taken away for a period of time, grounding them or taking away certain privileges. Offering a reward for effort, this may be in the form of a cash incentive for improved results or achieving a certain mark per subject, it could be purchasing them something they would like, it could be additional privileges. Reasoning with them, explaining the importance of developing a mature work ethic and achieving good results. This is something teenagers struggle to fully comprehend so some true-life examples of success and failure of family members and friends, when it comes to financial and career success, may be useful here. Go through university courses they may be interested in with them and show them what is required to qualify for the courses. I have found that many teenagers have no idea what is required to gain access to a career they wish to pursue. A reality check is sometimes all they need. Help them think about their future and what they want to achieve in life. It needs to be concrete as having a goal is a great motivator for hard work. Usually, it is the students who have no real vision for their future and what they would like to achieve who struggle to motivate themselves to study. They simply don’t get why it’s important and of value. “Exam time can be very stressful, but taking some time to consider how to make the next exam session less so, and working towards establishing a positive trajectory, can make all the difference for the future,” says Gerli.







